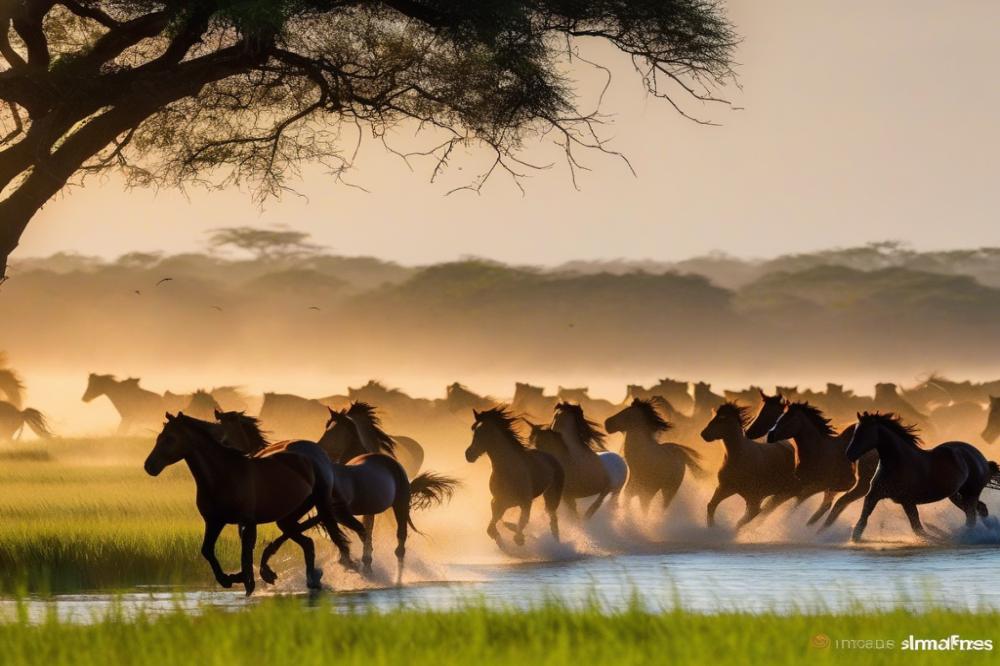
Brazil’s Feral Horses: Untamed Legacy in the Pantanal Marshes
Across the globe, wild horses roam through various landscapes, maintaining a bond with nature that few other animals share. These creatures embody a spirit of freedom that captivates many. In Brazil, one remarkable population exists within the Pantanal Marshes. This region is known for its rich biodiversity and stunning wetlands.
Brazil’s Feral Horses hold a special significance. They reflect a rugged history and cultural heritage that trace back to the arrival of Spanish settlers. Those horses adapted over the centuries, thriving in the unique ecosystem of the Pantanal. They play a role in maintaining the balance within their environment. Their grazing habits can influence plant growth, which, in turn, helps shape the habitat for countless other species.
The Pantanal marshes are more than just a home for these animals; they are a vital ecosystem. This extensive wetland hosts diverse species of flora and fauna. Various animals depend on the resources found in these marshes for survival. By coexisting with wild horses, this ecosystem benefits from their presence. Understanding their role in the Pantanal is crucial to appreciating the larger web of life there.
Feral Horses in Brazil
History of Wild Horses in Brazil
Horses were first brought to Brazil in the 16th century by Spanish and Portuguese explorers. From that moment, these animals began to roam freely across various landscapes. Over time, some horses escaped or were set free. This led to the establishment of feral populations. These wild horses adapted to different environments, but none more so than the Pantanal. The Pantanal is the world’s largest tropical wetland. It served as a natural habitat suited to their survival.
Introduction and Adaptation to the Pantanal Region
The Pantanal’s vast territory presents both challenges and benefits. With its marshes and grasslands, horses found plenty of food. Their ability to traverse waterlogged areas is impressive. This adaptability allows them to thrive despite harsh conditions. In addition, they have developed social structures similar to those of domesticated horses. Watching them move across the landscape highlights their connection to the land. The Pantanal’s climate, with its rainy and dry seasons, shapes their behavior. Herds often shift locations based on these seasonal changes.
Cultural Significance and Local Perceptions
Horses play a noteworthy role in local folklore and traditions. Many people see them as symbols of freedom and resilience. The image of wild horses is woven into stories, art, and local celebrations. For some, they represent a link to a past where the land was more untamed. Communities around the Pantanal often hold mixed feelings about these animals. While some cherish their wild spirit, others worry about their impact on local ecosystems. Balancing these perspectives takes ongoing dialogue. Educating locals about their ecological role may help foster a greater appreciation. The feral horses have become part of the Pantanal identity, reflecting both the beauty and complexity of this region.
Ecological Role of Feral Horses

In the lush expanses of the Pantanal marshes, feral horses play a significant role in the local ecosystem. Their grazing habits directly impact biodiversity. These animals help maintain the balance of various plant species. When they feed on certain grasses, they can prevent the dominance of invasive plants. This creates more space for native flora to thrive.
Interactions between horses and other wildlife are quite fascinating. Herbivores such as capybaras and deer share the same habitat. Their presence can lead to competition for food, influencing population sizes. Predators, such as jaguars and pumas, also notice changes when these horses are around. Their movements can affect hunting patterns, as predators adjust to this added variable in their environment.
Horses also influence plant communities. Through their movement, they can trample down areas of thick vegetation. This trampling creates open patches that allow sunlight to reach the ground. As a result, new plants can sprout in these areas. Consequently, these animals help maintain a diverse range of habitats that support various species.
Hydrology in the marshes can also shift due to feral horse activity. As the horses roam, they create paths in the landscape. Water can flow more freely in these areas, affecting nearby plant life. This change can benefit other animals that rely on those water sources. Their presence, therefore, not only shapes the environment but also impacts the entire food web.
Understanding their role is critical to preserving the rich complexity of the Pantanal. These horses are more than just a striking sight. They are an integral part of the ecosystem and contribute to its ongoing health and diversity.
Behavior and Social Structure
The wild horses in the Pantanal Marshes exhibit fascinating herd dynamics. Social behavior is critical to their survival in this difficult environment. Horses often form close-knit groups, typically composed of a dominant stallion, several mares, and their young offspring. The leader plays a vital role, guiding the herd to greener pastures and watering holes.
Communication among these animals is essential. They use a variety of vocalizations and body language to express emotions and warn of dangers. When startled, the herd reacts swiftly, often synchronizing their movements to escape threats. These instincts are crucial for survival in the face of predators.
Herd Dynamics and Social Behavior
The social structure is influenced by environmental challenges. In the marshy terrain, food and water sources can be scarce. This scarcity encourages collaboration among herd members. During dry spells, the group rallies to seek out sustenance together. Each horse has its role within the group, which fosters stability and security.
Colts remain with their mothers for several years, learning crucial skills. Social bonds between horses are strong, allowing them to recognize each other even after long separations. This connection among herd members fosters cooperation during critical times, especially when raising foals.
Adaptations to the Marshy Environment
Living in the wetlands necessitates adaptations. These horses have developed a keen sense for navigating through muddy grounds and shallow waters. Their thick coats help protect against both the heat and moisture. In addition, their strong legs are adapted to cover long distances in search of food and safety. These features give them an edge in this unique habitat.
Seeking shelter from the sun and rain is also important. During hotter days, they find shade under trees or bushes. This behavior not only cools them down but also helps avoid pesky insects that thrive in wet conditions. By being aware of their surroundings, they maintain their health in a challenging ecosystem.
Reproductive Strategies and Survival Instincts
When it comes to reproduction, timing is everything. The mating season often aligns with the rainy season, ensuring that foals are born when resources are more plentiful. This strategy allows young horses a better chance of survival. After birth, mothers protect their foals fiercely, often keeping them close at all times.
Survival instincts drive much of their behavior. Resting or grazing, they remain alert to potential dangers. Even while feeding, some horses will stand guard, eyes scanning the horizon for predators. This vigilance is crucial in an environment with various threats.
Overall, the interplay of these behaviors defines their existence in the Pantanal. Strong social bonds, adaptations to a harsh habitat, and effective reproductive strategies all contribute to their enduring legacy in this remarkable ecosystem.
Conservation Challenges
Threats to feral horse populations in Brazil
Wild horses face many threats in Brazil, especially in the vast Pantanal Marshes. Habitat loss is a significant issue. As agriculture expands, these animals have less space to roam. Competition for resources also arises. Domesticated livestock often outnumber the wild herds, leading to scarcity of food and water. In addition, climate change alters their environment, causing droughts that further diminish their survival chances. The delicate balance of this ecosystem can shift, endangering not just the horses, but other wildlife as well.
Balancing ranching practices and wildlife preservation
Ranching is a vital part of the economy in Brazil. Many ranchers rely on cattle for their livelihoods. However, this industry can conflict with wildlife needs. Sustainable practices are essential to protect both ranching and the native species. Some ranchers work to create wildlife-friendly areas. This cooperation can benefit both sides but requires genuine commitment. Striking a harmony between livestock and the wild horses is crucial for a healthy ecosystem. It is a delicate dance, one that demands understanding and effort from everyone involved.
Legal and ethical considerations for conservation
Conservation laws influence how wildlife is protected in Brazil. A framework exists to safeguard these horses, yet enforcement is often weak. Different stakeholders have various views on wildlife protection. Some see it as essential, while others prioritize economic gain. Ethical questions arise: Should economic interests take precedence over the survival of a species? When discussing conservation, these debates become critical. Balancing legal obligations and moral responsibility poses challenges. Thoughtful dialogue is necessary to work towards viable solutions that respect both the animals and the ranchers’ needs.
Conservation Efforts and Strategies
Current initiatives aim to protect horses roaming the Pantanal marshes. Several organizations focus on studying their impact on the ecosystem. Efforts include monitoring populations and their health. Surveys help gather vital information about their numbers and movements. Researchers examine how these animals interact with their environment. This data is crucial for forming effective conservation plans.
Role of Local Communities and NGOs
Local communities play a significant part in conservation work. Many residents understand the importance of preserving their heritage. They’ve begun to act as stewards of the land, working alongside researchers. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are also essential. They provide resources and training to help locals manage their natural surroundings. Education programs teach surrounding populations about the ecological value of these animals. By involving the community, efforts can be more sustainable in the long run.
Potential for Sustainable Ranching and Coexistence
Ranching offers a chance for farmers and wildlife to thrive together. Sustainable ranching methods can benefit both parties. Practices include rotational grazing and habitat management. These strategies reduce overgrazing while helping local biodiversity. Collaboration between ranchers and conservationists can lead to innovative solutions. By respecting the needs of wild animals, ranchers can maintain their livelihoods. This coexistence demonstrates that agricultural and environmental interests can align effectively.
Final Thoughts
The significance of Brazil’s wild horses extends beyond their beauty. They represent a connection to the region’s cultural and ecological history. Humans and nature have coexisted with these animals for generations. Their presence helps to maintain the balance of the local ecosystem, highlighting the interconnectedness of all living things. As a species that has adapted to the rugged terrain of the Pantanal marshes, they serve as symbols of resilience and strength.
Looking ahead, the future of these animals hinges on conservation efforts. Sustainable practices can help preserve their habitat and promote biodiversity. Local communities play an essential role. By understanding the benefits of protecting these animals, they can collaborate with conservationists and scientists. Education can bridge the gap between communities and the preservation of their unique heritage. It is vital that future initiatives focus on both wildlife and human development.
Raising awareness is crucial for the survival of these beautiful creatures. Individuals can make a difference by supporting organizations dedicated to conservation. Local tourism can also contribute, showcasing the importance of these wild horses and their habitat. Thus, it is essential to get involved. Advocating for responsible practices and spreading knowledge about these remarkable animals encourages the protection of this vital part of Brazil’s natural heritage.



