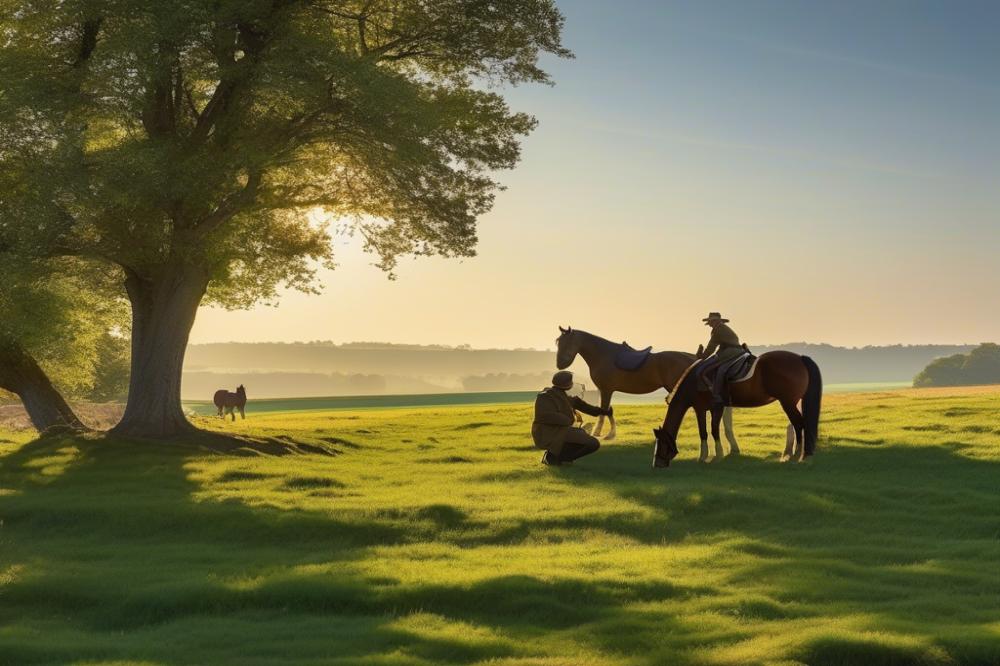
Introduction
Breeding techniques in horses play an essential role in equine management. Different methods exist, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these techniques helps breeders make informed decisions. Pasture Breeding and Hand Breeding are two common approaches that vary in process and outcome.
Breeding is important for improving genetics within a horse population. Selecting the right stallion and mare can lead to stronger offspring. Good genetic traits may enhance performance, health, and even temperament. As a result, breeders aim to produce the best horses possible.
Comparing Pasture Breeding and Hand Breeding offers insights into their effectiveness. Each method has distinctive characteristics that can influence breeding success. Evaluating these differences helps breeders choose the right approach for their specific goals and circumstances.
Understanding Pasture Breeding
Pasture breeding refers to a method where livestock, particularly cattle and sheep, mate freely in a natural environment. In this system, animals have the freedom to roam and choose their mates. This approach is often part of broader livestock management practices focused on animal health and productivity.
Within livestock management, this method can play a significant role. Farmers often find that allowing animals to breed naturally can reduce stress for both breeders and livestock. The emphasis here is on creating a balanced ecosystem where animals are adapted to their surroundings.
Natural mating systems offer several benefits. First, they can lead to increased fertility rates. When animals breed without intervention, they may choose mates based on genetic compatibility. This can result in stronger offspring, as animals naturally select mates with desirable traits.
Compared to traditional breeding practices, this method is less labor-intensive. Farmers do not need to monitor animals constantly or manage mating schedules meticulously. Over time, animals that succeed in this environment adapt and thrive, creating a herd that is more suited to the local conditions.
Additionally, these systems often contribute to improved animal welfare. Animals experience less stress without confinement and can exhibit more natural behaviors. In contrast, traditional breeding can sometimes disrupt these natural instincts and lead to lower overall health in livestock.
While both methods have their advantages, it’s essential to evaluate specific needs. Some farmers may prefer hand breeding for its controlled nature, while others might favor the benefits that come from natural systems. Each method has its own impact on animal genetics and herd dynamics.
Examining Hand Breeding

Definition of Hand Breeding
Hand breeding is a method where breeders actively control the mating of animals. Instead of allowing them to breed freely in a natural setting, humans intervene. This technique helps in selecting specific animals for reproduction.
Techniques and Methods Involved
Several techniques are common in hand breeding. Artificial insemination is one of the primary methods used. This process involves collecting semen from a male and inserting it into a female at the right time. Some breeders may also manage mating directly by bringing the male and female together.
Close observation is essential during the breeding process. Breeders monitor animals for signs of heat, when females are most receptive. Additionally, tracking the animals’ cycles can lead to better timings for mating.
Pros and Cons of Hand Breeding
This breeding method offers various advantages. Higher control over genetics can lead to better offspring quality. Breeders can often select desirable traits, such as size or disease resistance.
On the downside, hand breeding can require more time and effort. It can be labor-intensive, especially if many animals are involved. Stress might also occur in animals that dislike being handled or moved frequently.
Impact on Breeding Efficiency and Genetic Selection
Hand breeding can enhance breeding efficiency for certain goals. A focused approach allows breeders to reduce the chances of inbreeding. Through careful selection, they can create a more diverse gene pool.
Genetic selection becomes more straightforward with this method. Specific traits can be enhanced over generations. Breeders can strive for characteristics that meet market demands or improve animal health. Overall, this method plays a significant role in modern breeding practices.
Comparison of Pasture Breeding and Hand Breeding

Two common methods of animal breeding are pasture breeding and hand breeding. Each has its advantages and drawbacks. Understanding their differences can help make informed decisions.
Key Differences Between the Two Methods
In pasture breeding, animals breed naturally in a larger environment. This approach promotes natural behaviors and instincts. Hand breeding, on the other hand, involves human control over the mating process. Animals are often separated and introduced at specific times. This can create a more focused breeding effort.
Analysis of Breeding Efficiency and Outcomes
Efficiency in breeding can vary greatly between methods. Pasture breeding might lead to more unpredictable results. Without close observation, some matings may not take place. However, this method can produce a broader genetic diversity. Hand breeding often leads to higher conception rates. It allows for a strategic selection of mating pairs to meet specific goals.
Influence on Animal Husbandry Practices
The choice of breeding method affects overall management of the herd. With pasture breeding, farmers must create suitable environments. It requires monitoring health and well-being closely. In contrast, hand breeding can streamline other management tasks. This method may demand more time upfront but can save time later by ensuring better genetic outcomes.
Considerations for Selecting a Breeding Method
Several factors come into play when choosing a breeding strategy. The goals of the breeding program dictate the best approach. Farmers should consider the breed of the animals and their characteristics. Resources available, like land and time, also matter. Pasture breeding may be ideal for those with ample space and natural environments. For those with specific genetic goals, hand breeding often makes more sense.
Reproductive Strategies in Horses
Overview of Reproductive Cycles and Timing
The reproductive cycle of a mare typically lasts about 21 days. This cycle consists of several phases, including estrus, ovulation, and diestrus. Estrus lasts for approximately 5 to 7 days, during which a mare is receptive to a stallion. Ovulation occurs toward the end of this period, signaling the best time for breeding. Understanding these cycles helps breeders determine optimal breeding times. Monitoring these cycles can often lead to more successful breeding outcomes. Using technology like ultrasound can aid in detecting ovulation. Knowing when a mare is fertile is crucial for any breeding program.
Selection of Breeding Stock in Pasture versus Hand Breeding
When selecting breeding stock, the approach can vary greatly between pasture and hand breeding. In a pasture setting, mares and stallions are allowed to interact naturally, which can sometimes lead to unexpected pairings. Hand breeding allows for more controlled pairings based on specific traits and genetics. Selecting breeding stock based on conformation, temperament, and performance can guide this process. Careful consideration is important for both methods. Some breeders may choose to assess genetic backgrounds to enhance quality. This can lead to a more strategic breeding plan.
Strategies for Maximizing Genetic Potential
Maximizing genetic potential involves thoughtful planning. Breeders often examine lineage to reinforce desirable traits. This might include looking for successful ancestors in various disciplines such as racing or show jumping. For pasture breeding, allowing natural selection can yield remarkable results. The selection happens based on which pairs naturally mate well. In contrast, hand breeding focuses more on the specific characteristics desired. This might include performance traits or physical attributes. Breeders may also utilize genetic testing to identify strengths and weaknesses in their horses. Such analysis can influence decisions made about pairings, leading to more favorable outcomes. Each breeding method holds advantages that can be strategically employed to accomplish the breeder’s goals.
Pasture Management and Breeding Impact
Importance of Pasture Management in Breeding
Good pasture management plays a key role in breeding. Healthy grasslands provide essential nutrition for livestock. Animals need adequate forage to maintain their health and body condition. When cattle or sheep are well-fed, they are more likely to breed successfully. Proper grazing techniques can also help maintain the quality of pastures. Rotational grazing, for instance, allows areas to recover before animals return. This practice leads to better grass growth and soil health over time. Farmers who focus on pasture management often see improved reproductive rates.
Effects of Pasture Conditions on Breeding Success
Pasture conditions can greatly influence breeding success. Adequate water supply is crucial for livestock health and reproductive performance. If animals become dehydrated, stress levels rise, and breeding may suffer. Additionally, a well-timed pasture management plan can help in synchronization of breeding cycles. When pastures are lush and nutritious, animals tend to breed more readily and frequently. On the contrary, poor pasture conditions can lead to low conception rates. This makes it essential to monitor and adjust pasture health throughout the breeding season.
Integration of Livestock Management Practices in Breeding
Integrating livestock management practices is essential for effective breeding. Regular health checks ensure that animals are free from diseases that might affect reproduction. Nutrition management also plays a crucial part. Feeds enriched with vitamins and minerals support the overall wellbeing of livestock. Effective record-keeping helps farmers track breeding cycles and identify the best times for mating. Moreover, providing shelter and protection from harsh weather enhances an animal’s ability to conceive. Making holistic management decisions can have a lasting impact on breeding outcomes.
Applications in Other Livestock Breeding
Comparison with Cattle Breeding and Sheep Breeding
Cattle breeding often utilizes methods similar to those seen in pasture breeding. Cows can roam freely with bulls during the breeding season. This approach allows natural mating behavior to occur, which may contribute to successful pregnancy rates. Compared to sheep breeding, the methods are somewhat similar but have distinct differences. Sheep are often managed in smaller groups, allowing for easier observation. Some farmers prefer hand breeding for sheep because it gives them more control over genetics. This control can lead to improved flock quality. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses.
Lessons Learned from Pasture Breeding in Other Species
Observations from horse breeding show benefits that can apply to other types of livestock. Horses that breed in a natural setting often exhibit stronger maternal instincts. This can result in healthier foals. Various research indicates that animals raised in a more natural environment tend to adapt better. Breeders have noticed that stress levels drop, leading to a more successful reproductive cycle. Such insights can enhance cattle and sheep breeding practices. It is vital to understand how environment influences breeding outcomes.
Broader Applications of breeding techniques
Techniques from pasture breeding can help improve the overall productivity of farms. Incorporating rotational grazing can decrease land degradation while benefiting animal health. Such practices support better soil quality, which can indirectly boost livestock growth. Additionally, using these methods may reduce the need for veterinary interventions. Many livestock producers have found that balanced nutrition is essential. The integration of traditional practices with modern science offers a promising way forward. By utilizing these insights, farmers can develop a more sustainable approach to livestock breeding.
Final Thoughts: Comparing Breeding Methods
Summary of Key Points Discussed
When examining the two methods of breeding horses, several important factors come to light. Hand breeding offers close monitoring of the mare and stallion, which can result in higher success rates. This method allows for immediate assessment of the breeding process. On the other hand, pasture breeding promotes natural behaviors. The freedom to interact can sometimes lead to more successful matings. Additionally, this approach requires less direct human intervention. Each method has its own advantages and challenges.
Final Thoughts on Breeding Approaches
Every horse breeder must consider their specific situation. Factors such as location, horse temperament, and available facilities play crucial roles. For those who prioritize hands-on management, hand breeding may be the preferred choice. Conversely, those looking for a more relaxed, natural setting might lean towards pasture breeding. It’s essential to evaluate the individual needs of both the mare and stallion to choose the most effective method.
Recommendations for Horse Breeders
Breeders should take the time to understand the strengths and weaknesses of these breeding techniques. Conducting thorough research can aid in making informed decisions. An awareness of livestock management practices will further improve outcomes. Whichever method is selected, ensure that the health and welfare of the horses come first. Regular veterinary check-ups and proper nutrition are key in both breeding methods. Ultimately, a careful approach will foster successful breeding experiences.



